Laboratory for Water and Wastewater Technologies
UMTEC has various analytical devices and experimental setups to address issues in the fields of analytics as well as soil contamination, drinking water treatment, and wastewater treatment. Below, we present our most important devices.
Sample Preparation
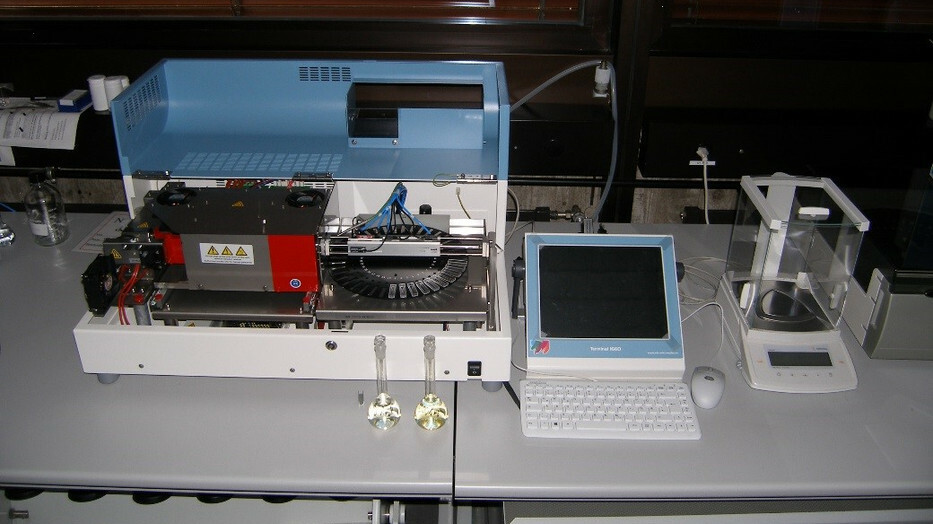
Microwave Digestion Device
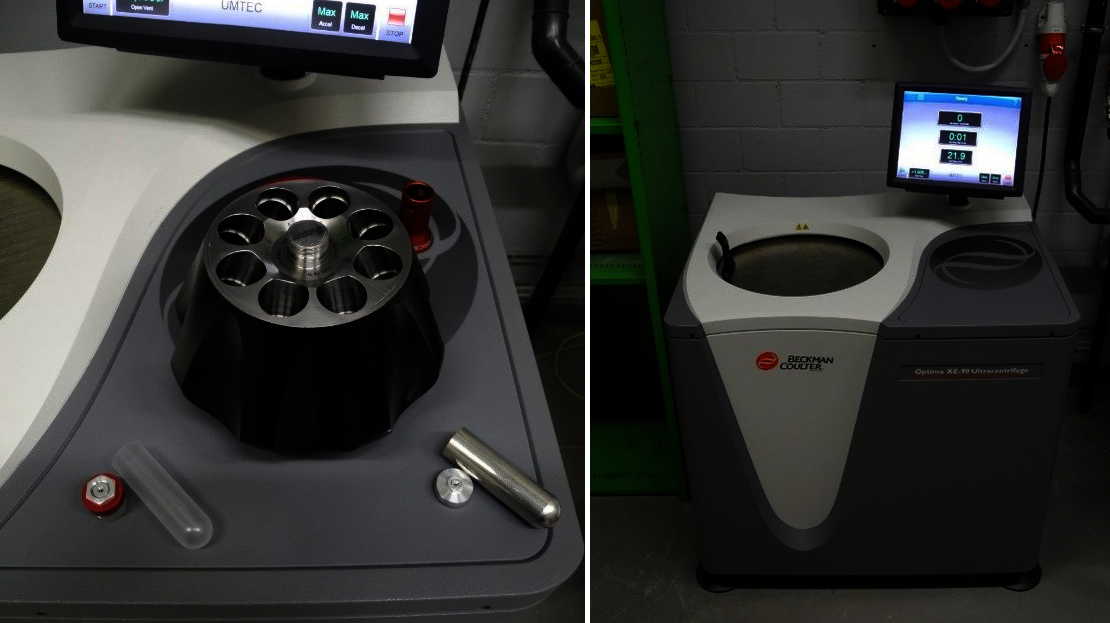
Ultracentrifuge and Tabletop Centrifuge
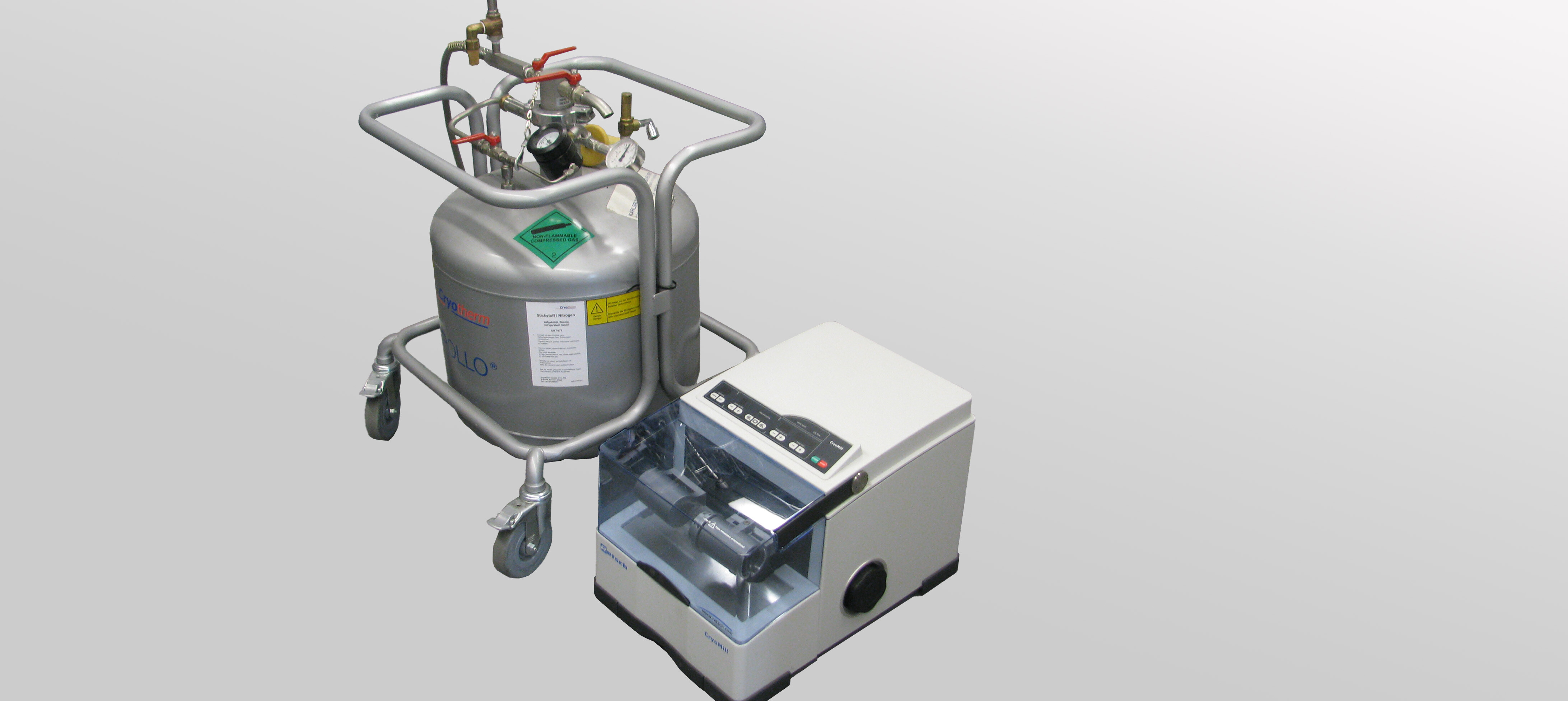
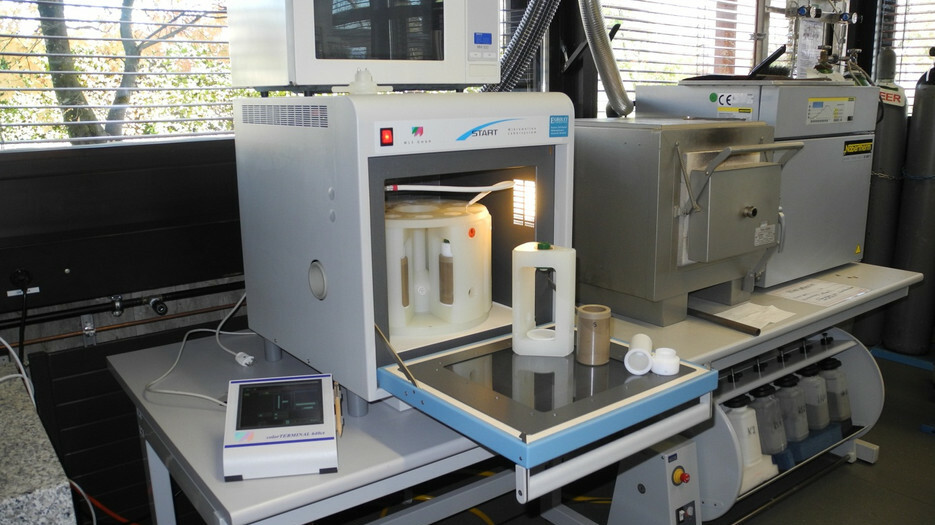
Cryogenic Mill (Retsch / Laboratory)
This vibratory mill, developed for cryogenic grinding, is suitable for the comminution of sample quantities up to 20 ml. By integrating cooling of the grinding jar with liquid nitrogen, the sample is embrittled at -196°C. This allows materials such as soft plastics to be ground. Another advantage of the cooling is that volatile substances in the sample are preserved.
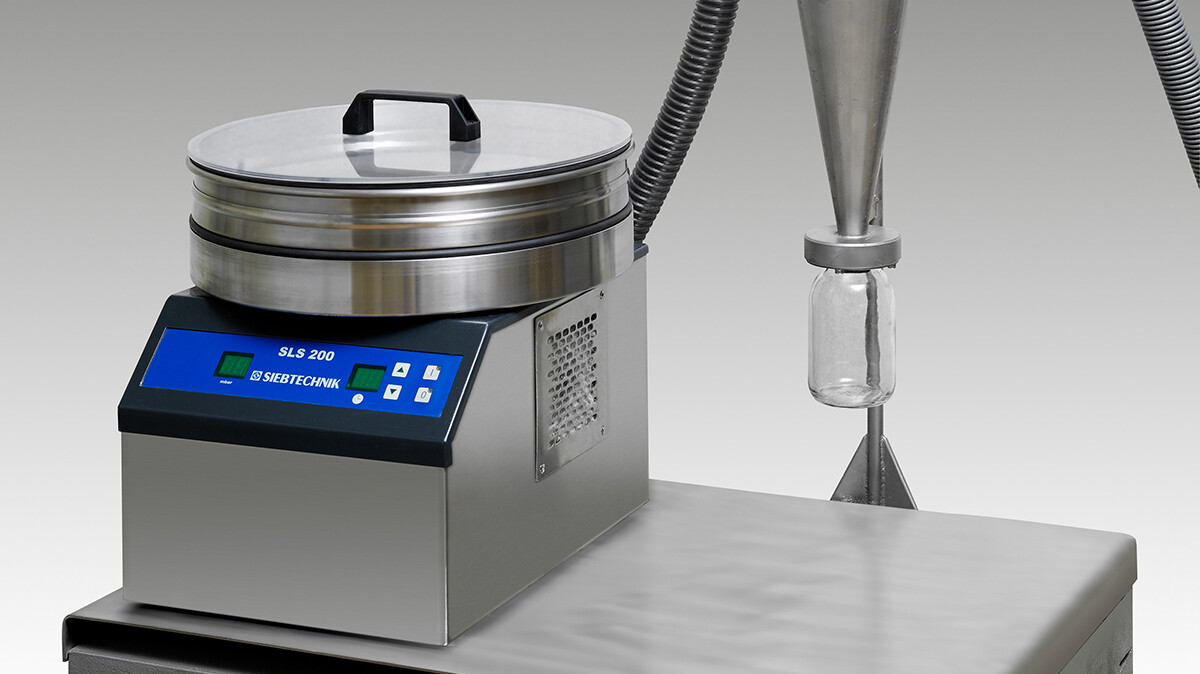
Air Jet Sieve
Planetary Ball Mill
Two planetary ball mills are available for sample preparation for chemical analysis. Using stainless steel or zirconium oxide grinding bowls and the corresponding grinding balls, particle sizes of less than 0.1 mm can be achieved, depending on the material being ground. Up to 125 ml of sample can be processed per grinding cycle.
Rotor hammer mill
Temperature-sensitive samples are ground in the rotor high-speed mill, as the rapid grinding minimizes the thermal stress on the material. A fast-running rotor with attached ribs breaks the sample by impact. Additionally, the sharp-edged teeth, in conjunction with the sieve, shear the sample. In the final grinding stage, the sample is subjected to friction between the rotor and the sieve.
Analysis
ICP-OES
Ion Chromatograph
The ion chromatograph (IC) is used for the quantification of ions in aqueous samples. It analyzes ions such as chloride (Cl-), ammonium (NH4+), nitrate (NO3-), nitrite (NO2-), phosphate (PO43-), sulfate (SO42-), and heavy metal ions.
Application example: Monitoring the effectiveness of precipitants for phosphate removal in municipal wastewater.
Mercury Analyzer
Photometer
The photometer can be used to determine various dissolved water constituents, such as chloride (Cl-), ammonium (NH4+), nitrate (NO3-), nitrite (NO2-), phosphate (PO43-), sulfate (SO42-), heavy metal ions, and dyes, as well as turbidity (FNU, NTU) in aqueous samples. UMTEC has three different devices available.
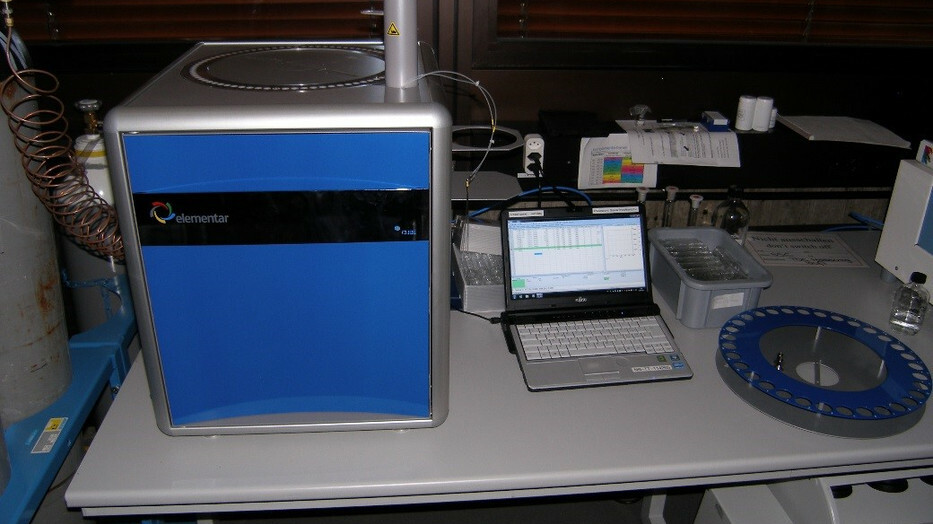
TOC/TNb Analyzer
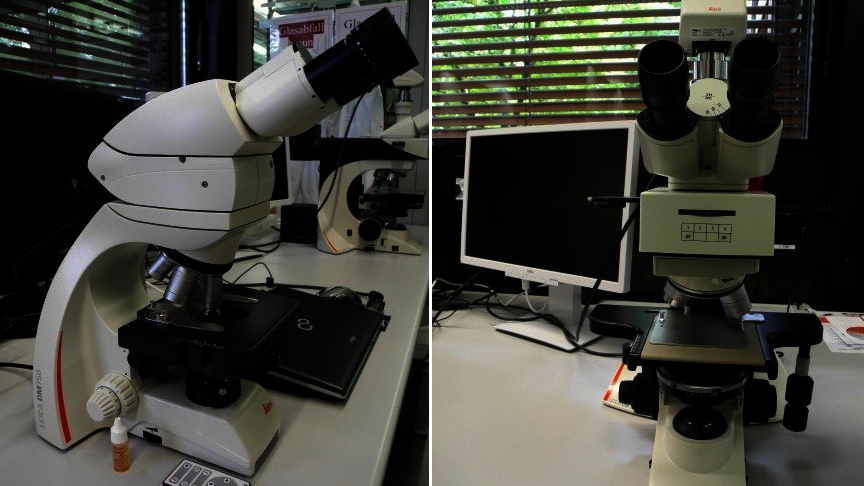
Light microscopes
For the qualitative assessment of liquid or solid samples, a transmitted light microscope and a reflected light microscope with digital cameras and image analysis software are available.
Application example: Morphological characterization of activated sludge from a wastewater treatment plant or filter materials.
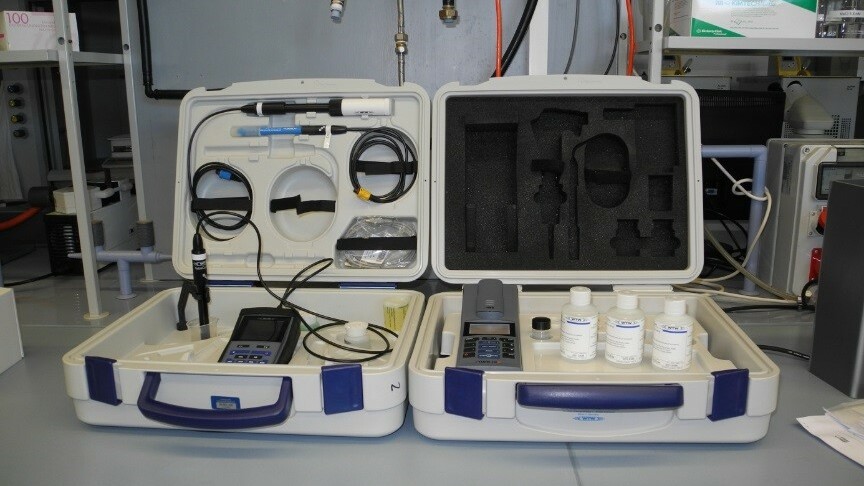
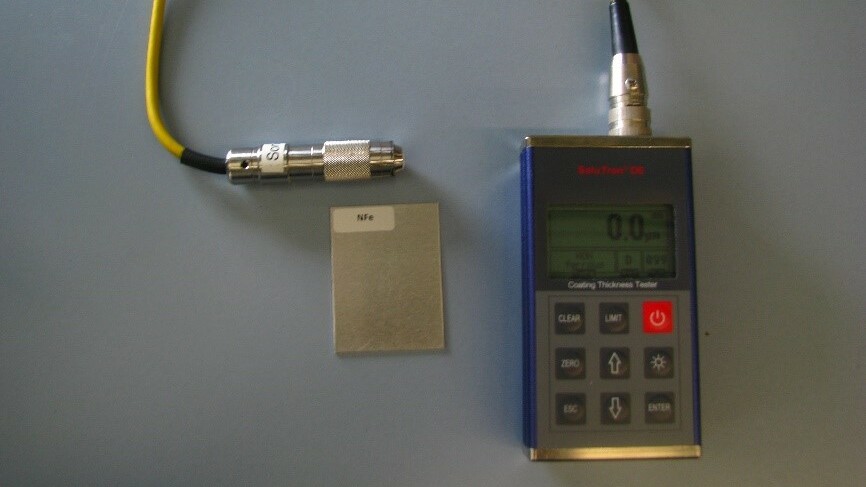
Handheld devices
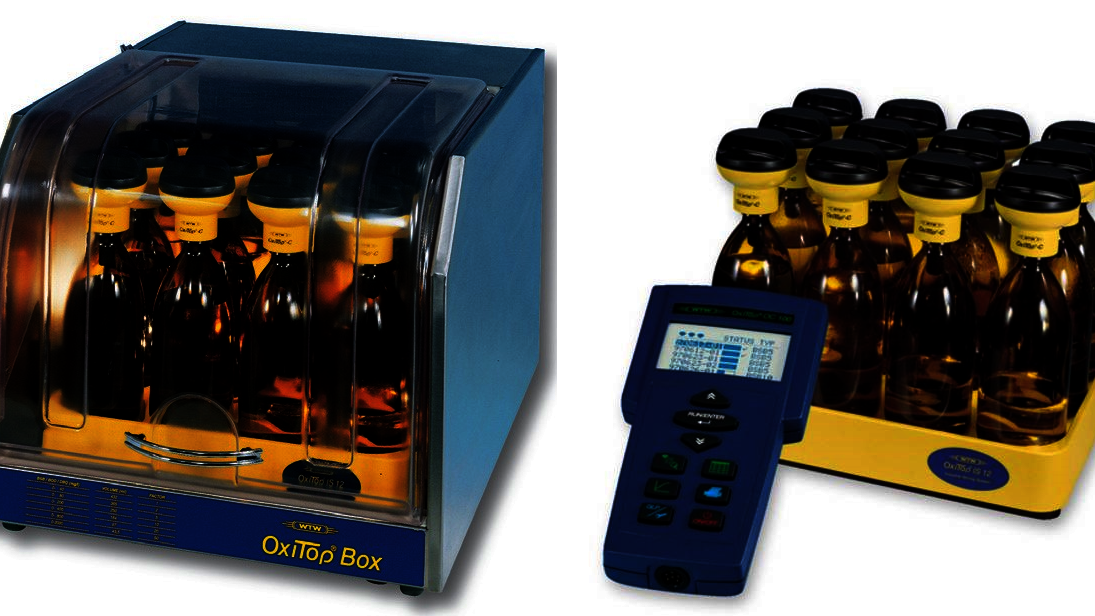
BSB - Measuring device
Test installations
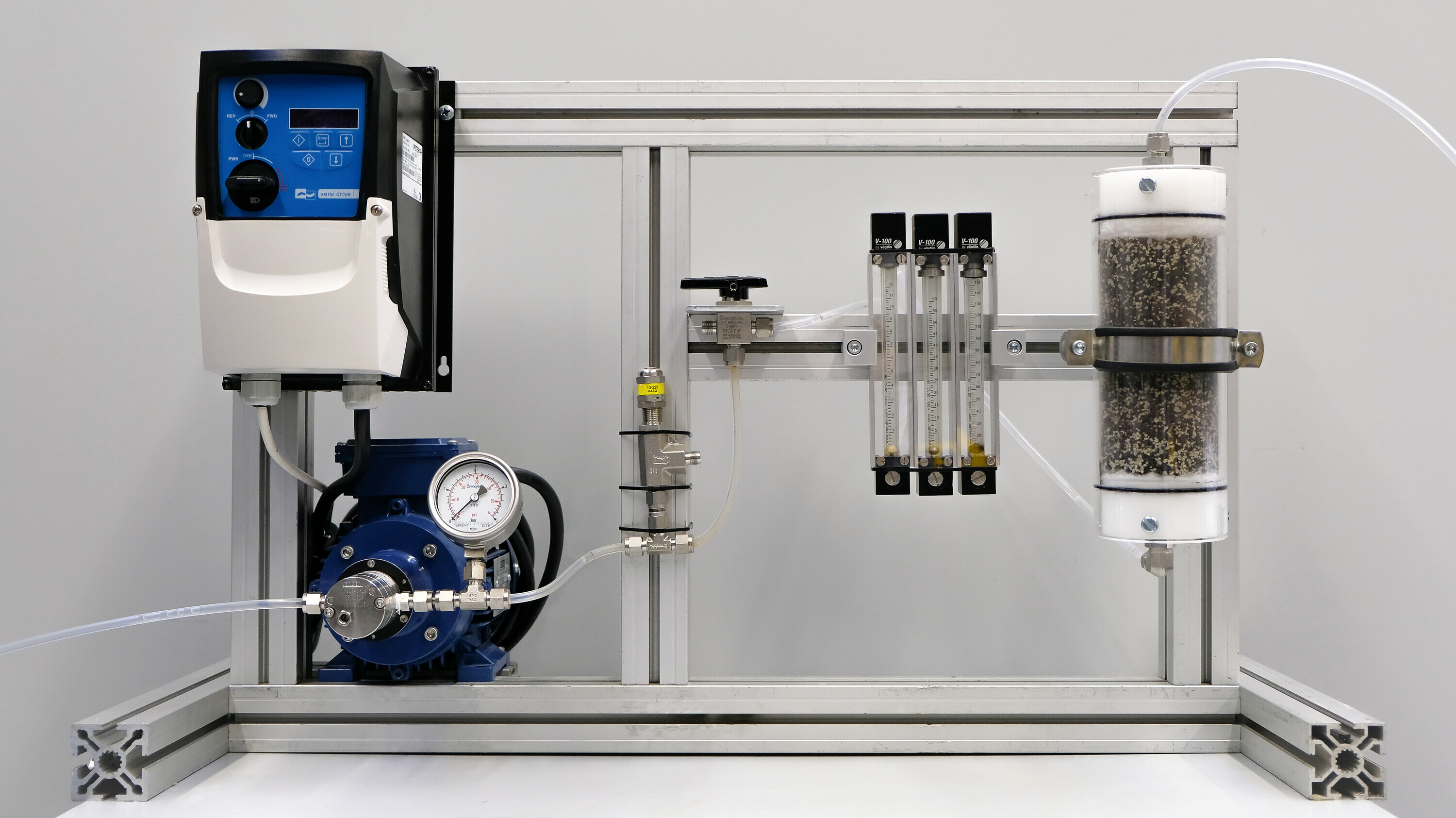
Column system
Lysimeter system
The lysimeter system is used to assess the migration behavior of substances under unsaturated conditions. The filling can consist of soil, slag, sand, etc. The substance to be studied is either applied directly or released from the material by irrigation. The 6 lysimeters (30 x 70 cm and 30 x 30 cm) can be equipped with pF, tensiometer, pH, temperature, and conductivity probes.
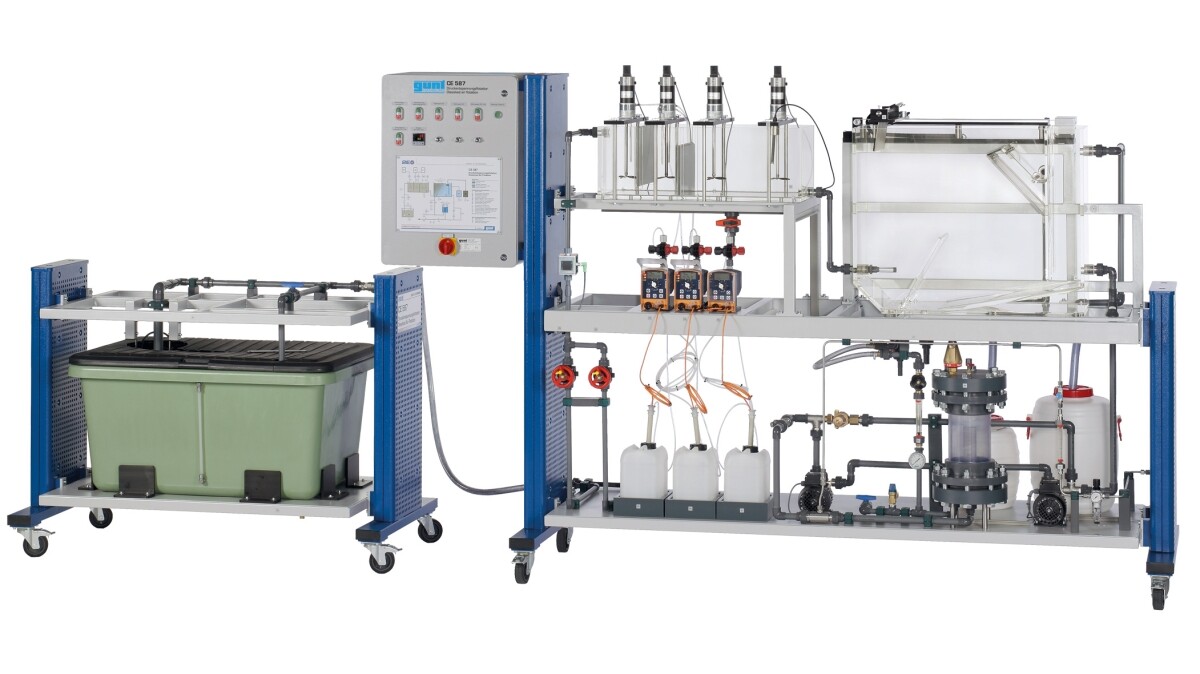
Flocculation and flotation system + lamella clarifier
A process engineering combination system for precipitation and pressure flotation of wastewater is used for demonstration and development projects. Numerous parameters, such as pH value, coagulant concentration, and flocculant aids, can be adjusted.
Application example: Process treatment of industrial wastewater.
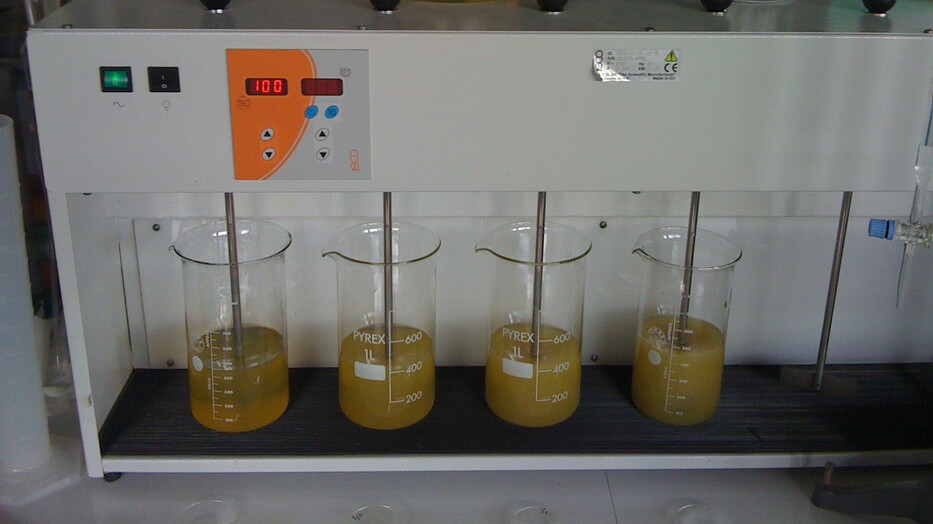
Flocculator (JAR-Test)
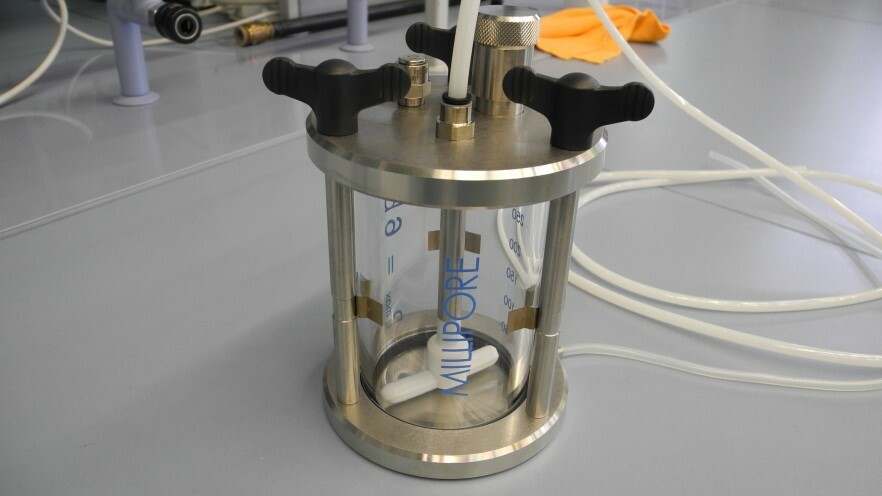
Membrane Test Cell Millipore
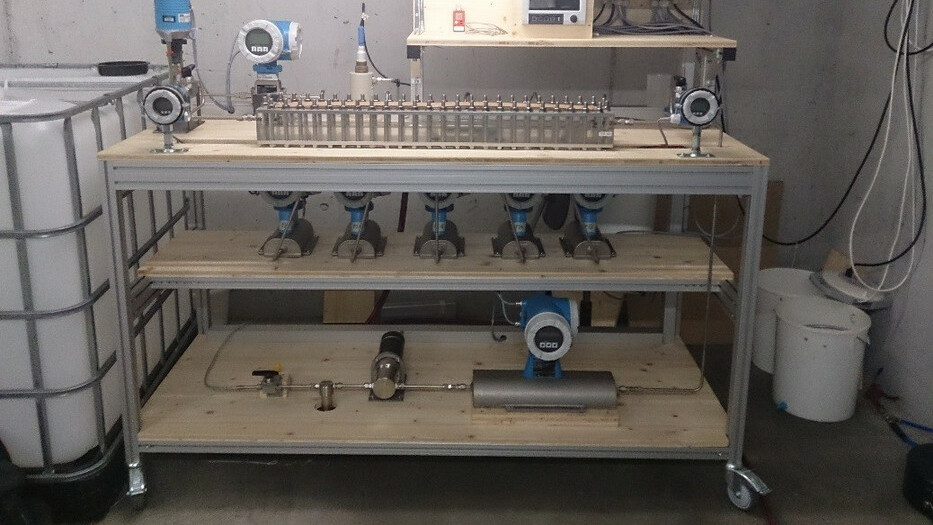
Membrane Test Stand Fouling
In the membrane test stand, based on the «Long Channel Membrane Test Cell» (LCMTC) from TU Dresden, flat membranes for microfiltration up to reverse osmosis, along with their spacers, can be tested for fouling behavior. A special feature is that the permeate can be continuously measured separately over five hydraulically separated segments using Coriolis flow meters.
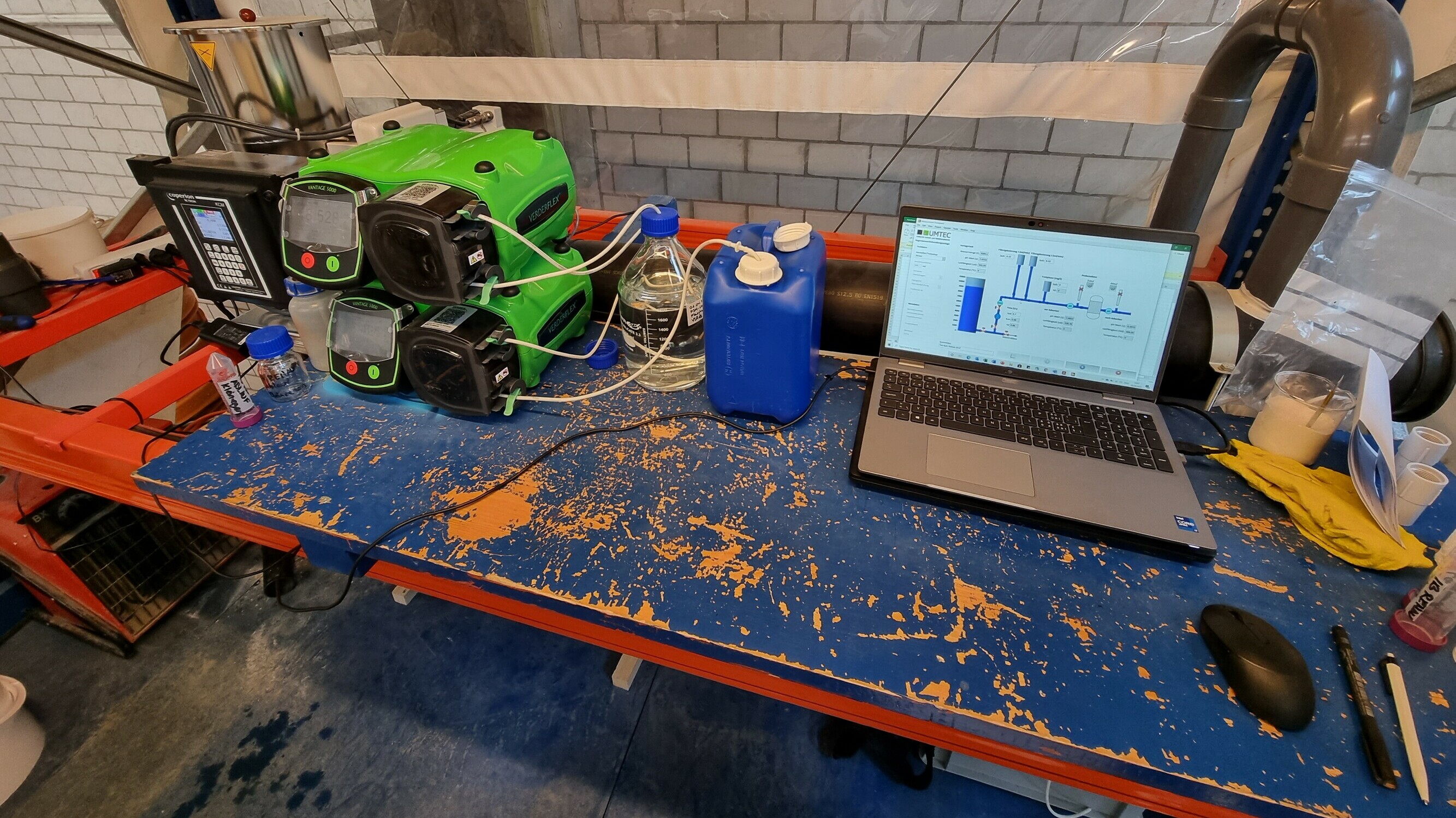
Rainwater Treatment System
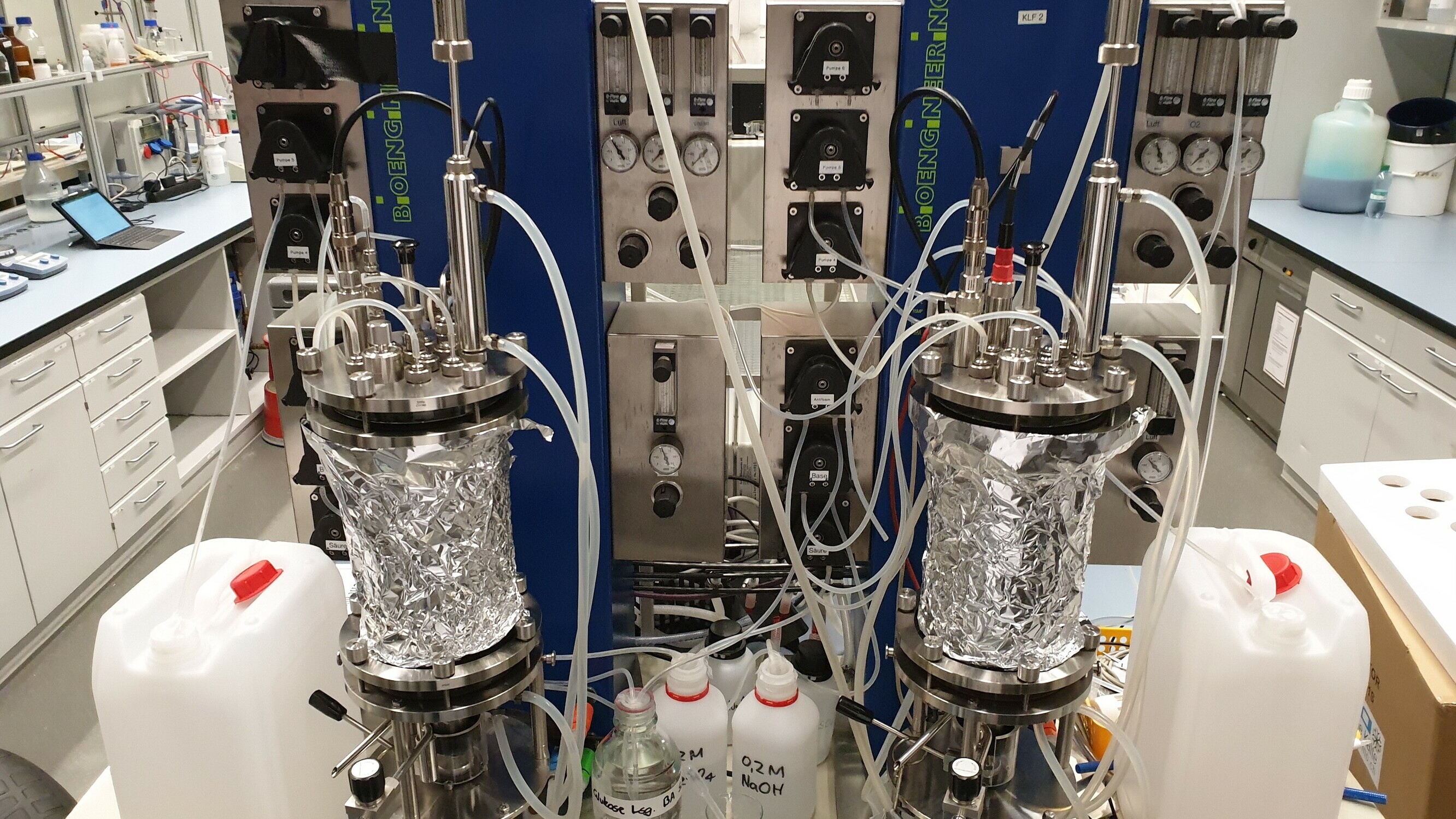
Laboratory Fermenter
Contact
Prof. Dr. Michael Burkhardt
Head of field Water and Wastewater Technology